
Benefits of Manual Therapy in Treating Back Pain Synapse PJ
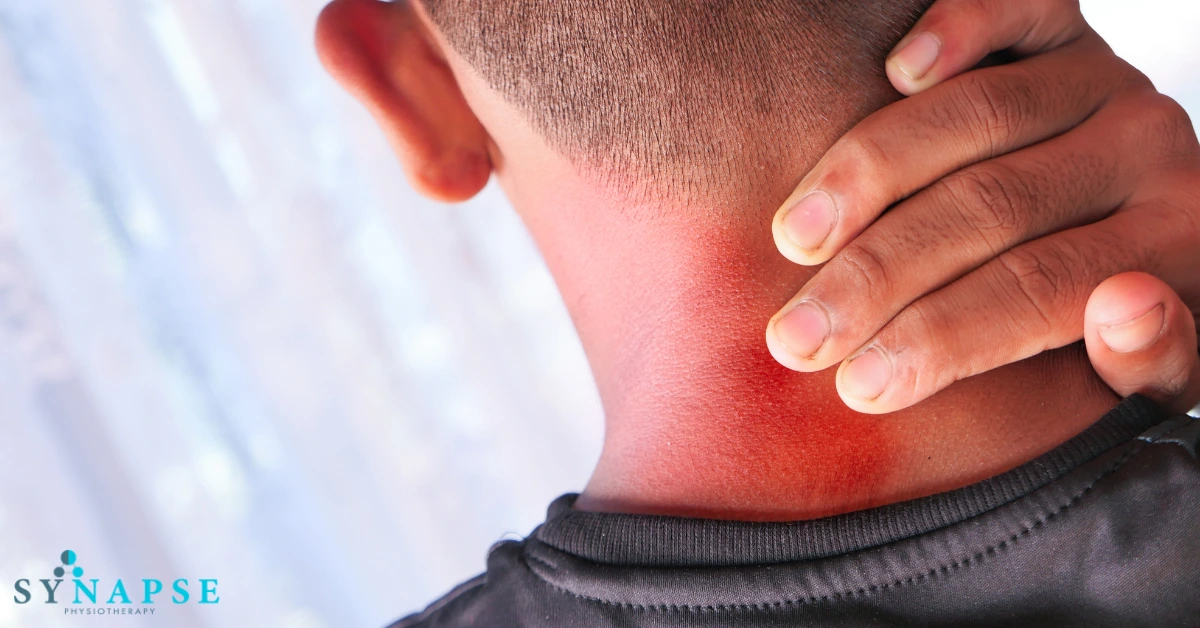
Back pain affects millions of people worldwide, making it one of the most common health complaints. While medications and surgeries are options, many are turning to non-invasive approaches like manual therapy for effective relief. For those experiencing back pain, it’s crucial to seek treatment immediately to prevent the condition from worsening. If you’re searching for local solutions, you might look for options like ‘physiotherapy PJ’ or nearby clinics offering specialized manual therapy services. This article explores the benefits of manual therapy in treating back pain, why it works, and how it can help you regain mobility and comfort.
What is manual therapy?
Manual therapy at physiotherapy Petaling Jaya has been the cornerstone of physical therapy for many years, evolving into a specialized approach to treat neuro-musculoskeletal conditions. It combines hands-on techniques, therapeutic exercises, and patient education to address pain, improve function, and promote overall wellness. Modern research highlights that manual therapy works through both physical and neurophysiological mechanisms, offering not just physical relief but also psychological benefits. This approach is guided by clinical reasoning, scientific evidence, and a personalized framework tailored to each patient at physiotherapy Petaling Jaya .
Techniques and benefits
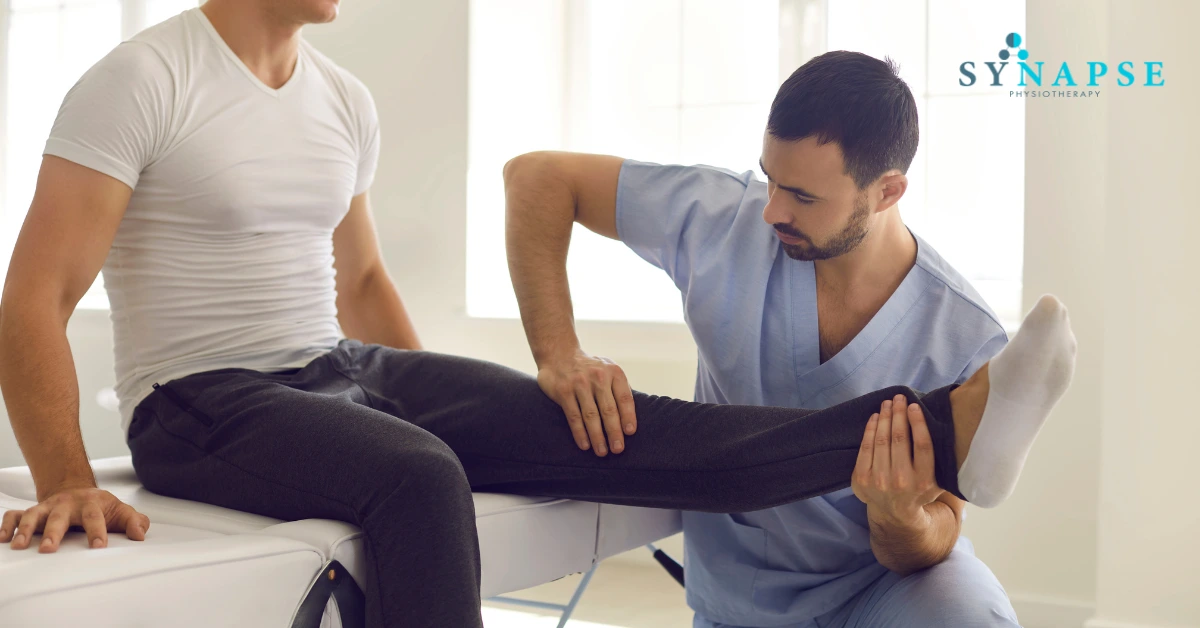
Joint mobilisation
Joint mobilisation is a manual therapy at physiotherapy Petaling Jaya technique used by physiotherapists to treat musculoskeletal dysfunction by improving restricted joint motion. It can address limitations in joints, connective tissues, or muscles, reducing the source of pain and providing relief. Gentle mobilizations are typically used to alleviate pain, while deeper, more forceful techniques help decrease joint stiffness and restore mobility.
Increasing Range of Motion
Joint mobilization helps improve the range of motion by gently stretching the fibrous tissue around the joint. This stretching causes a phenomenon called “creep,” where tissues temporarily change shape under constant pressure, allowing for increased mobility. Although the deformation is not permanent, the short-term effects can significantly enhance joint flexibility and function at physiotherapy Petaling Jaya.
Reducing Stiffness
For individuals with stiff joints that limit normal movement, mobilization techniques are used to target specific areas of restricted motion. Physiotherapists at physiotherapy Petaling Jaya assess the joint’s movement, identify the restricted range, and apply accessory mobilizations to address stiffness. Techniques such as staccato movements help maximize joint motion before neighboring joints engage, ensuring precise treatment. Adjusting the speed and intensity of mobilization based on the patient’s symptoms further enhances its effectiveness.
Alleviating Pain
In cases of severe pain limiting movement, joint mobilization offers symptom relief by positioning the joint in a comfortable, pain-free state. Oscillatory mobilization techniques are performed smoothly and evenly, ensuring minimal discomfort. By reducing pain, patients can regain mobility and participate in rehabilitative exercises more effectively.
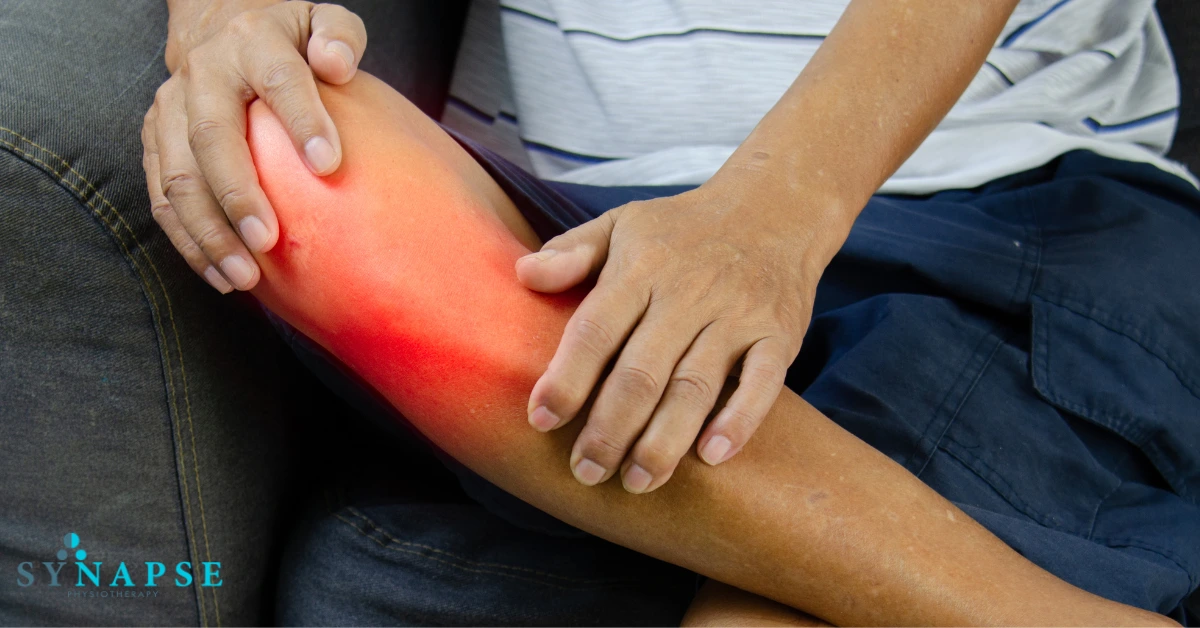
Soft Tissue Mobilization for Low Back Pain (LBP)
Soft tissue mobilization (STM) is widely used by clinicians to manage low back pain, leveraging various techniques to achieve pain relief and functional improvement. Let’s explore common STM methods, their evidence base, and when they are most effectively applied.
STM Techniques for Treating LBP
Soft tissue mobilization encompasses a range of methods, each targeting specific outcomes. Here are two widely used techniques for addressing low back pain:
Deep Tissue Massage
- This technique uses firm pressure to target deeper layers of muscles, tendons, or ligaments.
- Often applied to address chronic pain, friction massages—a type of deep tissue massage—are particularly effective for conditions involving tendinous or ligamentous structures.
- Advocates suggest it helps release muscle tension, improve blood flow, and alleviate pain associated with low back issues, though its application may vary depending on the individual’s condition.
Effleurage
- Effleurage involves long, smooth, and gentle strokes aimed at relaxing muscles and promoting overall circulation.
- This technique is commonly recognized as a “relaxing” massage and is often used for patients seeking relief from mild discomfort or stress-related tension in the lower back.
Reducing Pain
STM helps alleviate low back pain by targeting tight and inflamed soft tissues. It stimulates the release of natural pain-relieving chemicals in the body and activates pain-inhibitory pathways in the spinal cord and midbrain. This reduces pain signals, providing relief from both acute and chronic LBP.
Increasing Range of Motion
Restricted movement in the lower back is a common issue with LBP. STM stretches fibrous tissues and reduces stiffness in muscles and fascia, helping restore flexibility. Patients can perform daily activities more comfortably by improving mobility in the lumbar region.
Reducing Swelling
Swelling in the lower back due to injury or inflammation can exacerbate pain and stiffness. STM promotes the natural drainage of excess fluids through the lymphatic system, reducing swelling and enhancing tissue recovery.
Decreasing Muscle Adhesions
Muscle adhesions, or “knots,” in the lower back can limit movement and cause discomfort. STM breaks down these adhesions, allowing muscles to move freely and reducing the tension that contributes to LBP.
Speeding Recovery
Recovery from lower back injuries can be prolonged due to limited blood flow to the area. STM boosts circulation, delivering oxygen and nutrients to damaged tissues, which accelerates healing and reduces downtime.
Comparing Manual Therapy to Other Treatments
Manual therapy at physiotherapy Petaling Jaya offers a non-invasive alternative to medications, surgeries, and other treatment modalities for managing musculoskeletal pain, including back pain. Unlike medications, which may come with side effects such as drowsiness or dependency, manual therapy focuses on addressing the root cause of pain through hands-on techniques. While surgery can be effective, it involves higher risks, longer recovery times, and significant costs. Other therapies, like passive modalities or general exercise, may not provide the targeted benefits of manual therapy’s personalized approach. Many patients prefer manual therapy at physiotherapy Petaling Jaya for its holistic nature, minimal side effects, and ability to provide immediate relief while improving overall function.
Who Can Benefit from Manual Therapy for Low Back Pain?
Manual therapy at physiotherapy Petaling Jaya is a versatile treatment for individuals with low back pain, whether acute, chronic, or caused by injury or poor posture. For acute back pain, manual therapy provides relief by reducing muscle spasms and improving joint mobility. Chronic low back pain sufferers benefit from its ability to address stiffness, release muscle adhesions, and improve range of motion, helping to manage long-term discomfort. Those recovering from injuries like sprains or strains find manual therapy effective in accelerating healing, reducing scar tissue, and restoring function. Even individuals with postural imbalances due to prolonged sitting or poor ergonomics can regain alignment and reduce back strain through manual therapy, making it a comprehensive solution for all forms of low back pain.
Conclusion
Manual therapy at physiotherapy Petaling Jaya offers a targeted, non-invasive approach to alleviating low back pain, improving mobility, and enhancing quality of life. Whether you’re dealing with pain from an injury, posture-related issues, or chronic discomfort, this therapy can address the root causes and help you recover effectively. If you’re ready to take the first step toward a pain-free life, consult Synapse at physiotherapy Petaling Jaya. Our skilled physiotherapists specialize in manual therapy and tailored care, providing the treatment you need to restore function and regain comfort effectively. Contact us today to start your journey to recovery!
Tags :

Back & Neck Pain
- Spine & Core Rehabilitation
- Strength & Conditioning Programme
- Pain Management
- Biomechanical Assessment
- Sports Physiotherapy
- Group Class

Sports Injuries
- Strength & Conditioning Programme
- Pain Management
- Biomechanical Assessment
- Sports Physiotherapy
- Shockwave Therapy
- Group Class

Work Desk Injuries

Pre-Post-Surgical Conditions
Scoliosis & Postural Abnormalities

Neurological Conditions

Osteoarthritis & Rheumatism
Joint degeneration and inflammation happens as the human body grows older, but that does not mean our way of life degenerates as well. Relief your joint pains with a joint effort together with your physiotherapist, who will provide pain-relief treatments and prescribe exercises for your wellbeing.

Conditions Relating To Elderly
Common conditions in the older age population include hips & knee pain, back & neck pain, osteoarthritis, rheumatism, fear of falling and many more. Aging and degeneration of bodily function is inevitable, but here at Synapse, we will help you live the best of your life.