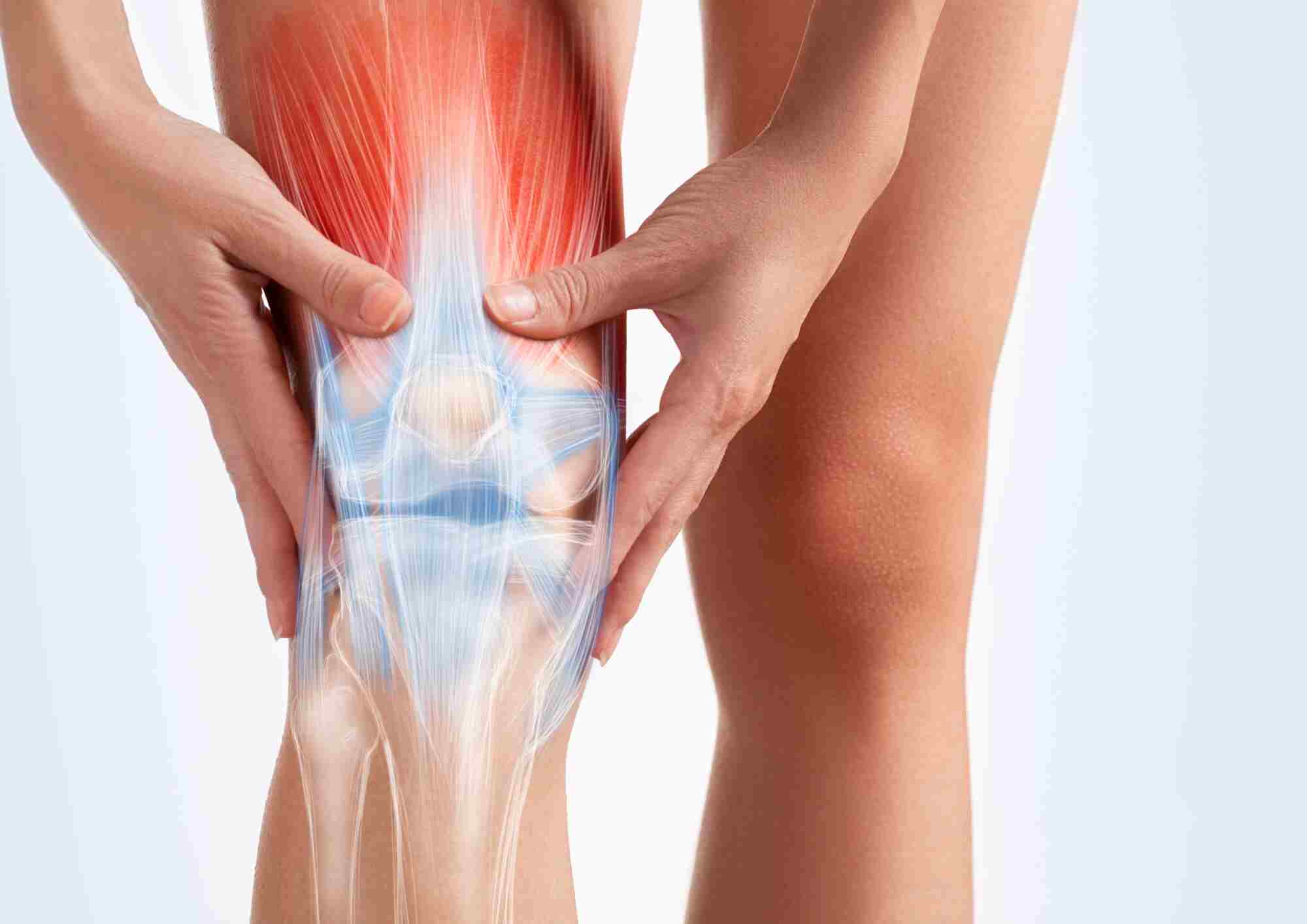

Fight Arthritis Pain Without Pills: Best Physiotherapy
Arthritis pain can be debilitating, but you don’t have to rely on pills to find relief. Best Physiotherapy offers a natural and effective solution for managing arthritis pain, helping you regain mobility, reduce discomfort, and improve your quality of life. In this article, we’ll explore the best physiotherapy treatments for arthritis and how they can make a significant difference in your pain management.
Understanding Arthritis and Its Impact
Arthritis is the swelling and tenderness of one or more joints. The main symptoms of arthritis are joint pain and stiffness, which typically worsen with age. The most common types of arthritis are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
- Osteoarthritis primarily damages the smooth cartilage lining of the joint, making movement more difficult, and leading to pain and stiffness. As the cartilage thins and deteriorates, tendons and ligaments must compensate, which can lead to swelling and the development of bony spurs called osteophytes. In severe cases, when cartilage is lost completely, bones may rub against each other, altering the joint’s shape and causing misalignment. The hands, knees, hips, and spine are the most commonly affected joints in osteoarthritis.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis is a less common form of arthritis that often develops between the ages of 30 and 50, with a higher incidence in women. This autoimmune disease causes the body’s immune system to attack the joints, leading to pain, swelling, and damage to the synovium, the outer covering of the joint. The inflammation can spread to the joint, causing further damage to the cartilage and bone. Rheumatoid arthritis can also lead to complications affecting other tissues and organs in the body.
Both types of arthritis can severely impact an individual’s daily life, but the best physiotherapy offers effective, non-invasive treatments to manage the symptoms and improve quality of life.
How Physiotherapy Helps Fight Arthritis Pain
Physiotherapy offers several benefits for individuals with arthritis, targeting pain relief, reducing inflammation, improving joint mobility, and enhancing overall function. By strengthening muscles and joints, the best physiotherapy helps slow the degeneration of affected areas, enabling individuals to manage arthritis symptoms more effectively. Here are the key benefits of physiotherapy for arthritis:
- Increase Joint Range of Motion:
Physiotherapy is highly effective in improving the range of motion in arthritic joints. Through a series of tailored exercises like flexion and rotation, physiotherapists work to enhance joint mobility, reduce stiffness, and increase flexibility. These exercises help to stimulate blood circulation around the affected joints, promoting healing and reducing discomfort. As joint mobility improves, it becomes easier for individuals to move freely and perform daily activities without pain or restriction. - Improve Balance:
Arthritis can affect balance, particularly in weight-bearing joints like the knees and ankles. Physiotherapy plays a vital role in improving balance by strengthening the muscles surrounding these joints. A personalized therapy program can help stabilize the body while walking, running, or performing other activities. The strengthening exercises target the muscles and joints to enhance stability, prevent falls, and make it easier for individuals with arthritis to move safely without the fear of instability. - Strengthen the Muscles:
One of the key aspects of the best physiotherapy for arthritis is strengthening the muscles around the affected joints. When arthritis causes swelling and limits movement, muscles can weaken, which further impairs joint function. Physiotherapists design specific exercises to progressively increase activity levels and strengthen the muscles in and around the joints. As the muscles become stronger, they provide better support to the joints, reduce pain, and improve overall joint function. A strong muscle foundation also helps prevent further joint damage, promoting long-term joint health. - Adjust Posture:
Arthritis can sometimes lead to postural problems or mild deformities in the affected joints.The best Physiotherapy is effective in correcting these postural issues, ensuring that the body is properly aligned and joints are positioned optimally. By focusing on posture correction, physiotherapists can help prevent additional strain on the joints, reducing pain and discomfort. In some cases, regular physiotherapy interventions can even reverse the effects of mild deformities caused by arthritis, allowing individuals to regain proper posture and function.
The overall goal of physiotherapy is to strengthen the muscles and joints, improving mobility, flexibility, and posture. By enhancing joint function and reducing pain, physiotherapy provides a holistic approach to managing arthritis, ultimately helping individuals lead more active and comfortable lives.
Best Physiotherapy Techniques for Arthritis Relief
Physiotherapy offers a variety of techniques to help alleviate arthritis pain, enhance joint mobility, and improve overall function. These methods are personalized to meet the unique needs of each patient. Here are some of the most effective physiotherapy techniques for arthritis relief:
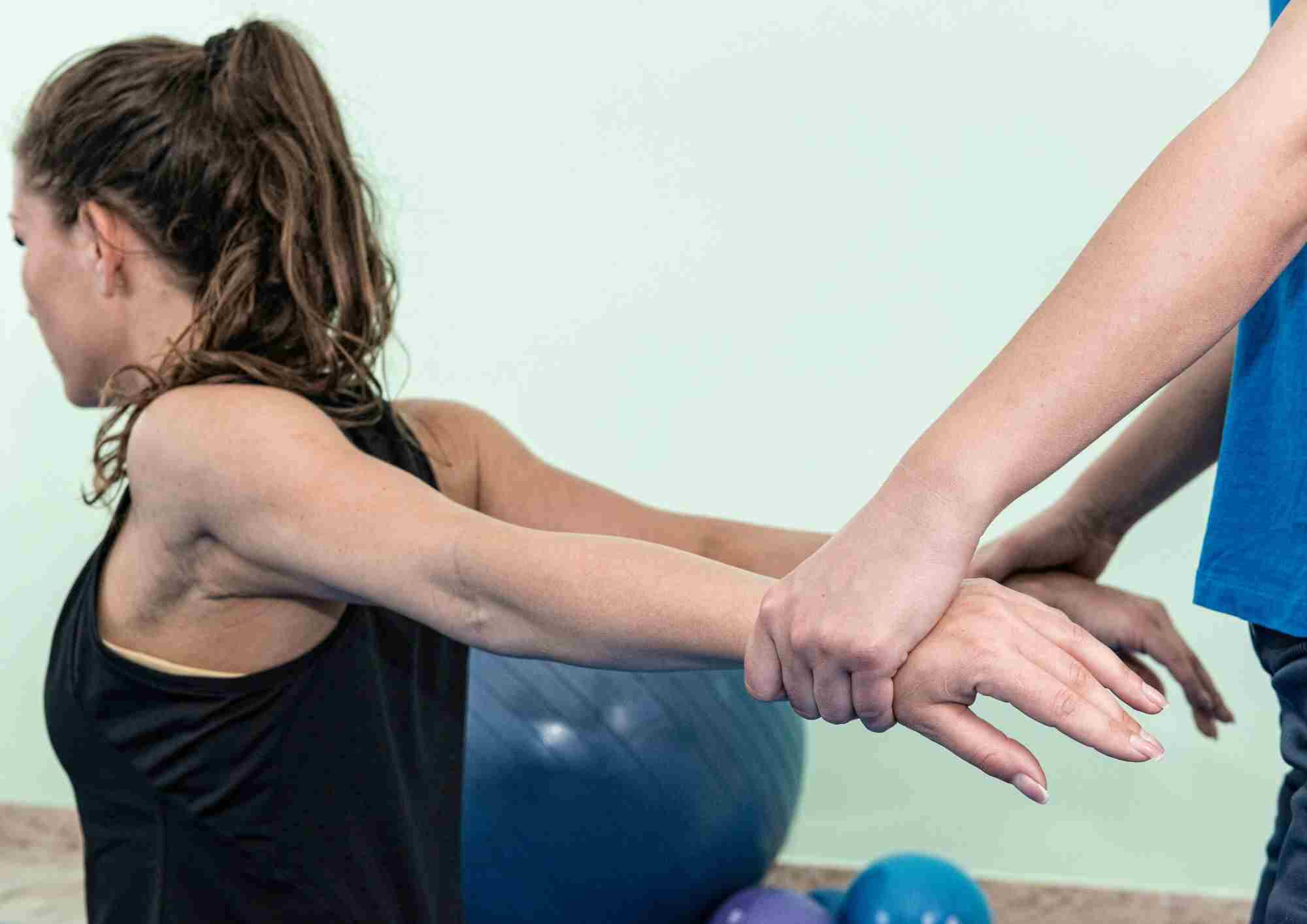
Personalized Exercises:
A tailored exercise program is essential for arthritis management, as it focuses on improving strength, mobility, and overall health. The following exercises are commonly included in physiotherapy programs:
- Stretching Exercises: These exercises are designed to ease aches and pains, helping to improve flexibility and encourage full-range movement of the joints.
- Strengthening Exercises: Aimed at building or maintaining strength in the muscles around the joints, these exercises help support the joints and reduce strain, improving stability.
- General Fitness Exercises: These exercises promote cardiovascular health and overall well-being, while also contributing to improved muscle tone and endurance.
- Proprioceptive Exercises: These exercises focus on improving balance, coordination, and agility, which are especially important for enhancing movement control and preventing falls.
- Hydrotherapy: This type of exercise is performed in warm water, which helps reduce the stress on the joints while improving flexibility, strength, and range of motion. The buoyancy of water also provides support and reduces the risk of injury during movement.
Pain Management Techniques:
Physiotherapy involves various methods to manage and reduce arthritis-related pain, helping individuals feel more comfortable and mobile:
- Ice Packs: Ice therapy reduces swelling in hot, inflamed joints and helps numb the area to provide immediate pain relief.
- Heat Packs: Heat therapy relaxes tense muscles and alleviates stiffness, improving blood flow and reducing discomfort in affected areas.
- Splints: These devices help stabilize swollen or painful joints, providing support and alleviating pressure.
- TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation): A small electronic device that sends pulses to nerve endings, altering pain signals and providing soothing relief from discomfort.
- Ultrasound Therapy: Sound waves penetrate deep into tissues, promoting healing and reducing inflammation, which is highly effective in pain management.
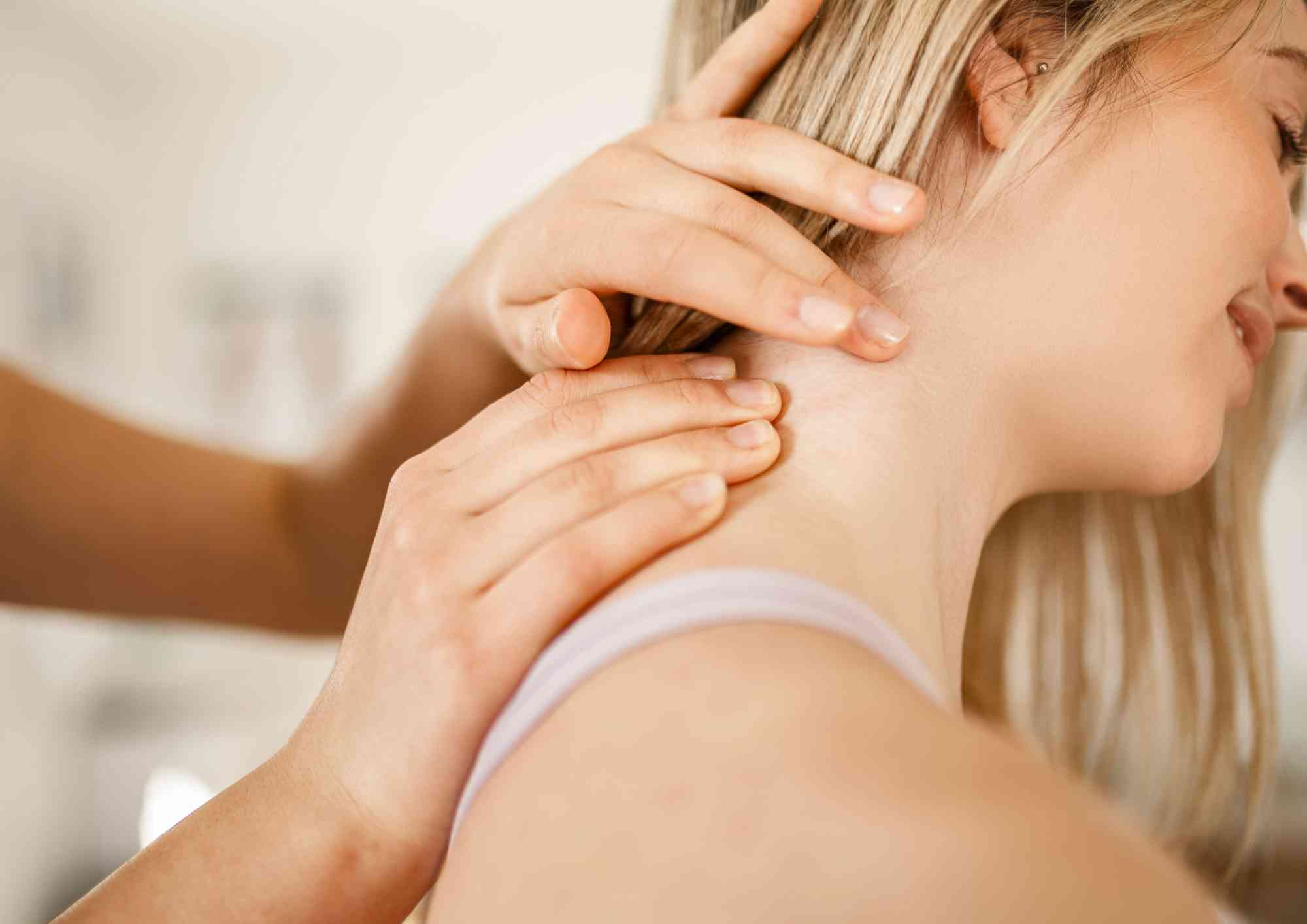
Manual therapy
- Massage /Soft Tissue Manipulation: Massage therapy helps relax muscles, reduce stiffness, and improve circulation in affected areas. Soft tissue manipulation techniques relieve muscle tension and promote relaxation, which can significantly reduce pain and improve joint mobility.
- Joint Mobilization: This manual therapy technique involves a physiotherapist using hands-on methods to move joints in a controlled manner. This helps reduce stiffness, improve range of motion, and promote better joint function.
When combined, these physiotherapy techniques create a holistic treatment plan that targets pain relief and functional improvement. By addressing both the underlying causes of arthritis and the symptoms, physiotherapy can significantly improve quality of life and help individuals manage arthritis more effectively.
When to See a Physiotherapist
If you’re struggling with arthritis pain and want to avoid relying on pills, it’s time to consider seeing a physiotherapist. Early intervention can prevent the condition from worsening and help you maintain a higher quality of life. If you experience joint pain, stiffness, or swelling, don’t wait for the symptoms to get worse—schedule a consultation with a physiotherapist to discuss a personalized treatment plan.
Conclusion: Embrace a Drug-Free Approach to Arthritis Pain
Physiotherapy is a powerful tool for managing arthritis pain without the need for medication. With personalized treatment plans, expert guidance, and the right techniques, you can relieve pain, improve joint function, and regain your mobility. At Synapse Physiotherapy, we offer customized care to help you lead a pain-free and active lifestyle. Start your journey to long-term relief today—consult with one of our qualified physiotherapists and embrace a drug-free approach to managing arthritis pain.
Tags :

Back & Neck Pain
- Spine & Core Rehabilitation
- Strength & Conditioning Programme
- Pain Management
- Biomechanical Assessment
- Sports Physiotherapy
- Group Class

Sports Injuries
- Strength & Conditioning Programme
- Pain Management
- Biomechanical Assessment
- Sports Physiotherapy
- Shockwave Therapy
- Group Class

Work Desk Injuries

Pre-Post-Surgical Conditions
Scoliosis & Postural Abnormalities

Neurological Conditions

Osteoarthritis & Rheumatism
Joint degeneration and inflammation happens as the human body grows older, but that does not mean our way of life degenerates as well. Relief your joint pains with a joint effort together with your physiotherapist, who will provide pain-relief treatments and prescribe exercises for your wellbeing.

Conditions Relating To Elderly
Common conditions in the older age population include hips & knee pain, back & neck pain, osteoarthritis, rheumatism, fear of falling and many more. Aging and degeneration of bodily function is inevitable, but here at Synapse, we will help you live the best of your life.






