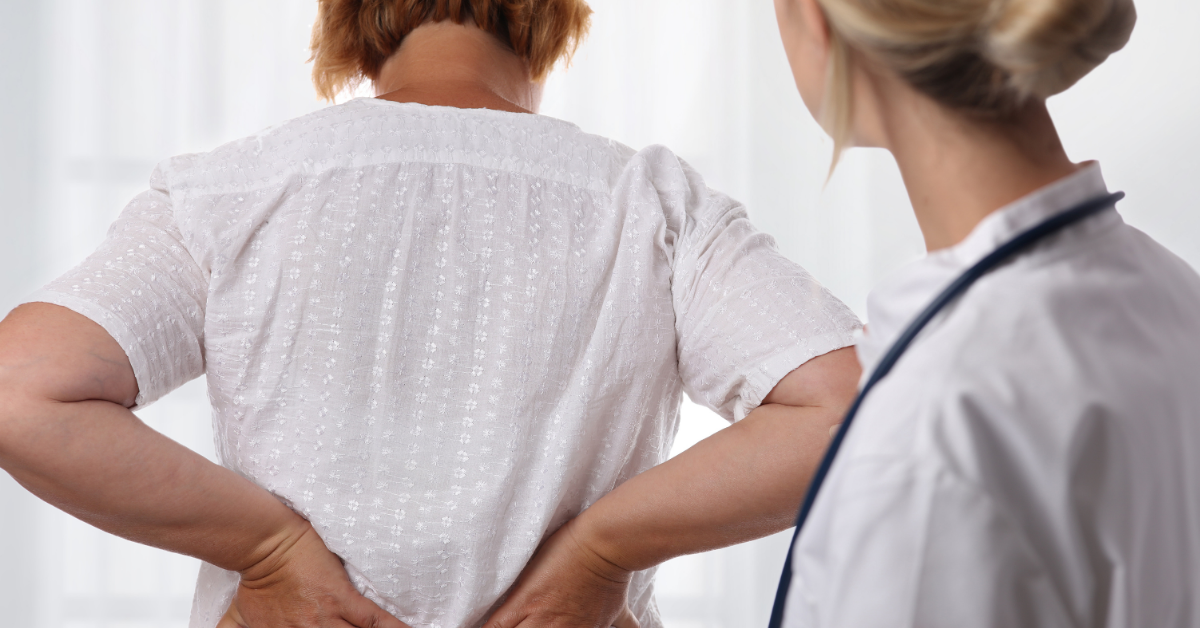

Back & Neck Pain, Synapse Physiotherapy
Introduction
Low back pain (LBP) is the fifth most common reason people visit doctors, affecting 60-80% of people at some point in their lives. Up to 23% of adults suffer from chronic LBP, with a recurrence rate of 24% to 80% within a year. Lifetime prevalence can be as high as 84%. LBP is defined as pain below the rib cage and above the legs. The most common type is “non-specific low back pain,” which has no identifiable cause. LBP is classified by duration: acute (less than 6 weeks), sub-acute (6-12 weeks), and chronic (more than 12 weeks). Chronic LBP, lasting over three months, accounts for over 80% of healthcare costs related to back pain. Nearly a third of people with acute LBP will have moderate pain a year later.
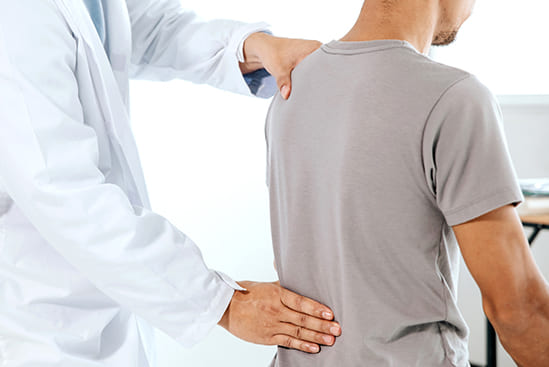
Physiotherapy is one of the best conservative treatments for low back pain. It offers various therapeutic techniques that can help alleviate pain, improve mobility, and strengthen the muscles supporting the spine. If you are experiencing low back pain, seeking help from a nearby physiotherapy center can be highly beneficial. To find a physiotherapy center in your area, you can use search engines and type in queries such as “physiotherapy Petaling Jaya” if you are located in Petaling Jaya. This will help you locate nearby physiotherapy clinics where you can receive the appropriate treatment and care. Regular sessions with a qualified physiotherapist can significantly contribute to your recovery and overall well-being.
Causes
Low back pain can result from various injuries, conditions, and diseases. Strains and sprains are the most common causes, often occurring from lifting heavy objects improperly or sudden movements like sneezing or bending. Fractures in the spine can happen due to accidents or conditions like osteoporosis. Disk problems, such as bulging or herniated disks, can press on nerves, while degenerative disk disease results from aging. Structural issues like spinal stenosis and scoliosis can cause significant pain and mobility problems. Arthritis, particularly osteoarthritis and ankylosing spondylitis, leads to inflammation and stiffness in the spine. Diseases like tumors, infections, kidney stones, and abdominal aortic aneurysms can also cause back pain. Spondylolisthesis, where vertebrae slip out of place, is another source of lower back pain.
Risk Factors
Lower back pain is influenced by several risk factors. Age is a significant factor, as people over 30 are more prone to back pain due to the natural wear and tear of the spinal disks, leading to pain and stiffness. Weight also plays a crucial role; individuals who are overweight or obese are more likely to experience back pain because the excess weight puts additional pressure on their joints and disks. Overall health is important too; weak abdominal muscles can’t adequately support the spine, leading to strains, while smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and a sedentary lifestyle further increase the risk. Occupation and lifestyle factors are also relevant, as jobs or activities that require heavy lifting or frequent bending can lead to back injuries. Structural problems, such as scoliosis, which alter the spine’s alignment, can cause severe back pain. Additionally, a family history of osteoarthritis, certain cancers, and other diseases can increase the risk of developing low back pain. Finally, mental health conditions like depression and anxiety can contribute to back pain.
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms of lower back pain can develop suddenly or gradually and may be triggered by specific events like bending the back to lift something, or they might occur without an obvious cause. The pain can vary from sharp to dull and achy, sometimes radiating to the buttocks or down the legs (sciatica). A “pop” sound might be heard if the back is strained during an activity. Pain often worsens in certain positions, such as bending over, and improves when lying down. Other symptoms include stiffness, making it difficult to move or straighten the back, especially when getting up from a seated position, and a decreased range of motion. People with back pain may struggle to stand up straight, resulting in a “crooked” or bent posture, with the lower back appearing flat instead of curved. Muscle spasms are also common, causing severe pain and making it difficult to stand, walk, or move.
Ways to prevent
Improving physical condition and learning proper body mechanics can help prevent back pain. To keep the back healthy and strong, regular exercise is essential. Engage in low-impact aerobic activities like walking, bicycling, or swimming to enhance strength and endurance without straining the back. Consult with a physiotherapist to determine the best activities for you. Building muscle strength and flexibility, particularly through abdominal and back exercises, is also crucial as it helps condition the core muscles to support the back. Maintaining a healthy weight is important since being overweight strains back muscles. Quitting smoking can reduce the risk of low back pain, with the risk decreasing as the number of cigarettes smoked per day decreases.
To avoid movements that twist or strain the back, use the body properly:
- Stand smart: Avoid slouching and maintain a neutral pelvic position. When standing for long periods, place one foot on a low footstool, alternating feet to reduce stress on the lower back.
- Sit smart: Choose a seat with good lower back support, armrests, and a swivel base. Use a pillow or rolled towel in the small of the back to maintain its natural curve. Keep knees and hips level and change positions frequently, at least every half-hour.
- Lift smart: Avoid heavy lifting when possible. If lifting is necessary, use your legs to do the work by keeping your back straight, bending only at the knees, and holding the load close to your body. Avoid twisting and find a lifting partner if the object is heavy or awkward.
Physiotherapy treatments
Physiotherapy treatments for low back pain encompass a diverse array of techniques aimed at reducing pain, enhancing mobility, and strengthening the muscles that support the spine. One of the key components is electrotherapy, which includes the use of interferential current (IFC). IFC employs low-frequency electrical currents to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation, providing relief from discomfort. Additionally, hot and cold packs are commonly used; hot packs help relax muscles and increase blood flow, promoting healing, while cold packs reduce inflammation and numb sharp pain, which can be particularly beneficial after acute injuries.
Ultrasound therapy is another valuable tool in physiotherapy. It uses sound waves to penetrate deep into tissues, reducing pain and inflammation and promoting tissue healing. This can be especially effective for chronic low back pain conditions.
Manual therapy is a hands-on approach that includes joint mobilization, which involves gentle, controlled movements to improve joint function and reduce pain. Myofascial release targets the fascia (connective tissue) to release tension and improve mobility. This technique is particularly useful for addressing muscle tightness and restricted movement.
For individuals with radiating pain, nerve mobilization techniques are employed to improve nerve function and reduce symptoms. These techniques involve specific movements and stretches that help mobilize the nerves, alleviating pain and discomfort that radiates from the lower back to other parts of the body.
Exercise therapy is a crucial component of physiotherapy for low back pain. Core stabilizing exercises are designed to strengthen the core muscles, providing better support and stability for the spine and helping to prevent further injuries. Stretching exercises are essential for reducing muscle tightness, especially in muscles that have become shortened due to poor posture. These exercises improve flexibility and help correct posture-related issues.
Strengthening exercises for the lower limbs, including the glutes, hamstrings, and quadriceps, are important for overall lower back support. Strong lower limb muscles help distribute the load more evenly and reduce strain on the lower back. Mobility exercises for the pelvic and lumbar regions are designed to enhance flexibility and reduce stiffness, promoting better movement and function in these areas.
Beyond these core treatments, physiotherapists may also incorporate education on proper body mechanics and posture correction to prevent future episodes of low back pain. Ergonomic advice for everyday activities and work environment can also be provided to minimize strain on the back. Additionally, therapeutic exercises can be tailored to individual needs, ensuring a personalized approach to recovery and long-term management of low back pain.
Overall, the comprehensive nature of physiotherapy, combining various techniques and individualized care, makes it a highly effective approach for managing and treating low back pain.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Low back pain can result from various injuries, conditions, and diseases, including strains and sprains from improper lifting or sudden movements, fractures, disk problems like bulging or herniated disks, degenerative disk disease, structural issues like spinal stenosis and scoliosis, arthritis, tumors, infections, and lifestyle factors such as obesity and smoking. Identifying the underlying cause is crucial for effective treatment.
Physiotherapy offers a diverse array of techniques aimed at reducing pain, enhancing mobility, and strengthening the muscles supporting the spine. These techniques include electrotherapy, hot and cold packs, ultrasound therapy, manual therapy, nerve mobilization, exercise therapy, and education on proper body mechanics and posture correction. By addressing the root causes of pain and promoting healing, physiotherapy can effectively manage and treat low back pain.
Exercise therapy is a crucial component of physiotherapy for low back pain. Core stabilizing exercises, stretching exercises to reduce muscle tightness, strengthening exercises for the lower limbs, and mobility exercises for the pelvic and lumbar regions are all beneficial. These exercises help strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, correct posture-related issues, and enhance overall lower back support.
Adopting healthy lifestyle habits can help prevent low back pain. Regular exercise, particularly low-impact aerobic activities like walking, bicycling, or swimming, helps strengthen muscles and improve flexibility. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces strain on the back, while quitting smoking decreases the risk of back pain. Practicing proper body mechanics when standing, sitting, and lifting heavy objects also helps prevent back injuries.
Seeking physiotherapy treatments for low back pain can significantly enhance recovery and alleviate discomfort. Physiotherapy offers tailored treatments that address the root causes of pain, promote healing, and strengthen the muscles supporting the spine. By opting for professional physiotherapy services, individuals can achieve better long-term outcomes, maintain a healthier, pain-free lifestyle, and prevent future episodes of low back pain.
Conclusion
In conclusion, seeking physiotherapy treatments when experiencing low back pain can significantly enhance recovery and alleviate discomfort. Physiotherapy offers a range of tailored treatments, including electrotherapy, manual therapy, and exercise therapy, all designed to reduce pain, improve mobility, and strengthen the muscles supporting the spine. Synapse Physiotherapy, for example, provides personalized treatment plans that cater to the specific needs of each patient, ensuring effective and comprehensive care. By opting for professional physiotherapy services, individuals can achieve better long-term outcomes and maintain a healthier, pain-free lifestyle.
Produced by MYSense
Tags :

Back & Neck Pain
Conditions such as stiffness, postural abnormalities and muscle overuse from prolonged desk work at the office or home is more prevalent than most would think. We provide the necessary tools to fix you up and educate you on ergonomics which can unload unnecessary stress.
- Spine & Core Rehabilitation
- Strength & Conditioning Programme
- Pain Management
- Biomechanical Assessment
- Sports Physiotherapy
- Group Class

Sports Injuries
Rolled ankles, jarred knees, impinged shoulders are few conditions in the plethora of sports injuries which can hamper performance and limit our enjoyment of sports. Physiotherapy not only treats the symptoms of these conditions but propels your overall fitness to greater heights.
- Strength & Conditioning Programme
- Pain Management
- Biomechanical Assessment
- Sports Physiotherapy
- Shockwave Therapy
- Group Class

Work Desk Injuries
Conditions such as stiffness, postural abnormalities and muscle overuse from prolonged desk work at the office or home is more prevalent than most would think. We provide the necessary tools to fix you up and educate you on ergonomics which can unload unnecessary stress.

Pre-Post-Surgical Conditions
Surgery involves going through preparation both before and after. Physiotherapists play a vital role in getting your body ready for surgeries with circulatory, breathing and strengthening exercises. After the procedure, let us be there for your recovery and rehabilitation, taking it one step at a time.
Scoliosis & Postural Abnormalities
The way we stand, sit, walk and sleep has influence over our posture and the overall balance of muscles controlling its alignment. A comprehensive screening can be done by our physiotherapists to detect abnormalities, which we will aid in correcting.

Neurological Conditions
Neurological disabilities such as stroke, nerve compression and neuropathies can be barriers for patients to live life to its fullest. We at Synapse are committed to help you overcome these hurdles by ensuring functional mobility and quality of life is at its optimum by providing the right treatment and exercises.

Osteoarthritis & Rheumatism
Joint degeneration and inflammation happens as the human body grows older, but that does not mean our way of life degenerates as well. Relief your joint pains with a joint effort together with your physiotherapist, who will provide pain-relief treatments and prescribe exercises for your wellbeing.

Conditions Relating To Elderly
Common conditions in the older age population include hips & knee pain, back & neck pain, osteoarthritis, rheumatism, fear of falling and many more. Aging and degeneration of bodily function is inevitable, but here at Synapse, we will help you live the best of your life.

Home Physiotherapy
We understand that some conditions or injuries can make it difficult to receive rehabilitation at our clinic be it mobility or transportation issues. Our objective is to provide you with the same high-quality physiotherapy services at home that you would receive in-clinic.
