
Synapse Physiotherapy
Introduction
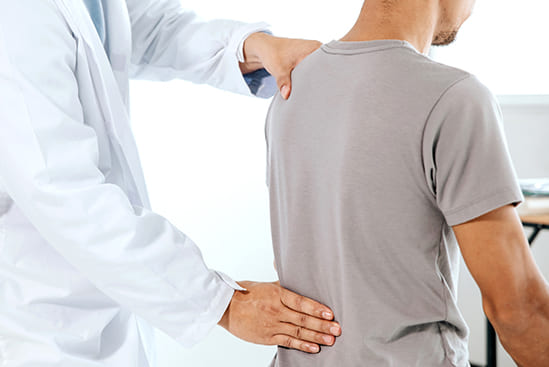
Joint pain refers to discomfort affecting one or more of your body’s joints. A joint is the point where the ends of two or more bones meet, such as the hip joint where the thigh bone connects to the pelvis. This type of discomfort is commonly experienced in the shoulders, hips, or knees. The pain can be constant or intermittent, and joints may feel stiff, achy, or sore. Some individuals report a burning, throbbing, or “grating” sensation. Often, joints feel stiff in the morning but improve with movement and activity, although excessive activity might exacerbate the pain. Joint pain can impair joint function and limit your ability to perform everyday tasks, severely affecting your quality of life. Treatment should aim not only at alleviating pain but also at enabling you to resume daily activities and live life to the fullest. When experiencing this type of pain, you may seek help from physiotherapy in Malaysia to receive treatment. Physiotherapy plays an important role in managing and treating knee, hip, and shoulder pain.
Knee pain
Causes
Knee pain can result from various types of injuries, including strains, sprains, ligament tears (such as ACL injuries), cartilage tears, or fractures. These injuries might occur from improper landing, falls, twisting the knee, or impact injuries like being hit on the knee. Swelling around the injured area is the primary source of pain.
Factors such as aging, being overweight, and engaging in intense, repetitive exercise can also contribute to knee pain.As you age, the bones and joints in your hips, knees, and feet begin to degenerate, becoming weaker. This degeneration can lead to knee pain, swelling, and injury. Being obese places additional pressure on the knees, which can result in swelling and pain.
Overuse injuries, often caused by activities like running, jumping, or other exercises that put repeated pressure on the knee, can develop over time. This condition is sometimes referred to as “runner’s knee.” Patellar tendinitis involves inflammation of the tendon connecting the kneecap to the shinbone. Tendons are tough bands of tissue that connect muscles to bones, and overexertion can lead to their inflammation and soreness. This condition, also known as “jumper’s knee,” is frequently caused by repetitive jumping activities, such as in basketball. IT (iliotibial) band syndrome occurs when the iliotibial band, a tough tissue running from the hip to the outer knee, becomes inflamed due to excessive activity. This causes pain on the outer side of the knee and is common among runners, particularly when running downhill. Then, osteoarthritis, also known as the “wear and tear” type of arthritis, breaks down the cartilage in the knee. It is a leading cause of knee pain in people over 50. This condition causes the knee joint to ache or swell during activity, and the affected joints can also be stiff in the morning.
Symptoms
You may experience knee pain, especially when bending or straightening the knee, such as when going down the stairs.Swelling, difficulty bearing weight on the knee, and trouble moving the knee are also common. Additionally, you might encounter knee buckling or “locking.”
Treatments
Cryotherapy, also known as cold therapy, involves the local or general application of low temperatures in medical treatment. It is used to treat various types of tissue damage, medically referred to as lesions.
Hydrotherapy, also known as hydropathy or water cure, uses water for pain relief and treatment. Its therapeutic purpose is to stimulate blood circulation and alleviate disease symptoms.
Manual therapy is a physical treatment provided by a physiotherapist. It focuses on treating musculoskeletal pain and disability through techniques such as kneading and manipulating muscles and joints to improve mobility.
Electrotherapy uses electrical energy as a medical treatment. It is applied in physical therapy to relax muscle spasms, prevent and slow disuse atrophy, increase local blood circulation, and aid in muscle rehabilitation and education through electrical muscle stimulation. Electrotherapy is also effective in managing acute post-traumatic and post-surgical pain, stimulating muscles immediately after surgery to prevent venous thrombosis, promoting wound healing, and aiding in drug delivery. Common forms of electrotherapy include TENS, IFT, and UST.
Exercise therapy is a regimen of physical activities designed and prescribed to achieve specific therapeutic goals, primarily aimed at restoring normal musculoskeletal function. This treatment helps reduce pain from injury or disease through neuro-education, gait training, and therapeutic exercises. It includes various physical activities such as quadriceps strengthening, VMO (vastus medialis oblique) exercises, muscle strengthening, resistance exercises, and assistive exercises.
Hip Pain
Causes
Hip pain can result from a variety of conditions, including arthritis, hip injuries such as fractures, labral tears, and dislocations, as well as bursitis and structural issues. Athletes who engage in activities involving extensive hip movements, like dancers and gymnasts, are particularly susceptible to hip injuries and the associated pain.
Arthritis, a common cause of hip pain, leads to inflammation and discomfort in the joints, resulting in symptoms such as pain, swelling, and stiffness. Types of arthritis that can affect the hips include osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis.
Bursitis, characterised by painful swelling of the bursa—a fluid-filled sac that cushions bones and other tissues—can also cause hip pain. Irritation and swelling of the hip bursa, known as hip bursitis, commonly occur in two forms: iliopectineal bursitis and trochanteric bursitis.
Hip injuries, often caused by repetitive strain, sports-related activities, or traumatic incidents like falls or accidents, can result in significant hip pain. Common injuries associated with hip pain include muscle strains (especially hip flexor strains), iliotibial band syndrome, hip labral tears, bone fractures, and hip dislocations.
Some individuals are born with structural abnormalities affecting the shape of their hips, which can lead to hip pain either in childhood or later in life. These conditions include femoroacetabular impingement (FAI or hip impingement) and developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH).
Overall, the causes of hip pain are diverse and can affect people of all ages, from athletes to those with congenital conditions, impacting their daily activities and quality of life.
Symptoms
Hip pain can manifest in several ways. It may be felt close to the surface, above or around your hip, which typically indicates issues with muscles, tendons, or ligaments. Alternatively, deeper pain inside the hip joint suggests problems with bones or cartilage. Sometimes, hip pain can radiate to other areas such as your lower back or groin.
The pain may be intermittent, worsening with movement or activity like walking but improving with rest. Some individuals experience variations in pain throughout the day, possibly feeling more discomfort in the morning upon waking. Hip pain at night is also common, particularly if lying on the same side as the affected hip.
Treatments
Physiotherapy treatments for hip pain are diverse and tailored to the specific cause of the discomfort. These treatments often include hydrotherapy, which involves exercises and activities performed in the water to alleviate pain and enhance mobility. Massage therapy is also utilised to manually manipulate muscles around the hip, reducing tension and improving circulation for healing. Core stability exercises are crucial for strengthening the muscles surrounding the abdomen, lower back, and pelvis to bolster stability and support for the hip joint. Taping techniques can be applied to provide support, alleviate pain, and promote proper movement patterns. Personalised exercise programs are designed to enhance strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the hip joint. Additionally, electrotherapy (such as TENS and ultrasound therapy) which utilizes electrical energy for pain relief, muscle relaxation, and stimulation, is often employed to manage hip pain effectively. These comprehensive physiotherapy approaches aim to reduce pain, improve hip function, and enhance overall quality of life for individuals suffering from hip discomfort.
Shoulder pain
Causes
Shoulder problems can be categorized into four main types, each with its own distinct characteristics and causes. First, tendon issues such as bursitis or tendinitis are common, affecting the small fluid-filled sacs (bursae) that cushion joints like the shoulder. These conditions can cause inflammation and pain, particularly with overhead activities. Tendon tears, either partial or complete, often result from acute injuries or degenerative changes due to aging or overuse, affecting tendons like those of the rotator cuff or biceps.
Shoulder impingement occurs when the acromion (top of the shoulder blade) compresses the rotator cuff tendons and bursa during arm movements, leading to bursitis and tendinitis. This can cause significant pain and limit movement. Instability of the shoulder joint can result from acute injuries, causing the upper arm bone to partially (subluxation) or completely (dislocation) come out of the socket. Chronic instability can lead to recurrent dislocations, increasing the risk of arthritis and causing pain and unsteadiness with arm movements.
Less common causes of shoulder pain include tumors, infections, and nerve-related issues. Arthritis, especially osteoarthritis, is a prevalent cause of shoulder pain, typically developing with age and characterized by pain and stiffness that worsen over time. Avoiding shoulder movements to ease arthritis pain can lead to further stiffness and reduced mobility, exacerbating discomfort.
Symptoms
Shoulder pain can manifest in various ways depending on its underlying cause. Whether in motion or at rest, common symptoms include weakness, aching or throbbing sensations, stiffness, soreness, and popping sounds. Severe shoulder pain typically resulting from an injury may present with sudden onset, sharp stabbing pain, and a limited ability to move the arm. Other signs of severe shoulder pain include swelling, bruising, persistent pain that worsens over time, and discomfort that disrupts sleep or wakes you up at night.
Treatments
Physiotherapy for shoulder pain involves a comprehensive range of treatments aimed at alleviating pain, restoring mobility, and improving the function of the shoulder joint. A typical physiotherapy regimen includes manual therapy techniques such as joint mobilisations to improve range of motion and soft tissue mobilisations to reduce muscle tension. Strengthening exercises target the muscles around the shoulder, including the rotator cuff and scapular stabilizers, while stretching exercises enhance flexibility and reduce stiffness. Modalities such as heat or cold therapy, and electrotherapy like TENS or ultrasound, are used to manage pain and inflammation. Physiotherapists also provide education on posture correction, activity modification, and home exercise programs to empower patients in managing their shoulder pain effectively. Using a combination of these approaches, physiotherapy aims to optimize shoulder function, decrease pain, and improve the overall quality of life for individuals suffering from shoulder pain.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can physiotherapy provide a permanent solution to joint pain?
While physiotherapy can significantly reduce joint pain and improve function, the permanency of results can vary depending on the underlying cause. For some chronic conditions, ongoing treatment may be necessary to maintain benefits.
2. How long does it typically take to see improvements from physiotherapy for joint pain?
Improvements can be seen as early as a few sessions, but it typically takes several weeks of consistent treatment to achieve significant pain relief and functional improvement. The exact duration depends on the severity and nature of the condition.
3. Do I need a referral from a doctor to see a physiotherapist for my joint pain?
In Malaysia, you do not typically need a referral from a doctor to consult a physiotherapist. However, having a referral can be helpful as it provides the therapist with valuable information about your medical history and the specifics of your condition.
4. What causes pain in the knees, hips, and shoulders?
Pain in these joints can be caused by a variety of factors including injuries, arthritis, repetitive stress, overuse, and age-related wear and tear. Specific conditions like bursitis, tendonitis, and mechanical issues also contribute to joint pain.
5. How can physiotherapy help relieve pain in the knee, hip, and shoulder?
Physiotherapy helps by using techniques such as manual therapy, exercises, and modalities like ultrasound or electrical stimulation. These methods improve mobility, strengthen muscles around the joints, reduce inflammation, and alleviate pain.
Conclusion
In conclusion, physiotherapy stands out as one of the most effective conservative treatments for various joint pain problems. Using a combination of manual therapy, exercise programs, and therapeutic modalities, physiotherapy aims to alleviate pain, improve joint function, and enhance overall quality of life. Physiotherapy also provides personalized care for conditions like shoulder, back, or knee pain, addressing the root cause and promoting long-term healing. For those seeking relief from joint pain, exploring physiotherapy, Synapse Physiotherapy can provide a comprehensive and tailored approach to recovery.
Tags :

Back & Neck Pain
Conditions such as stiffness, postural abnormalities and muscle overuse from prolonged desk work at the office or home is more prevalent than most would think. We provide the necessary tools to fix you up and educate you on ergonomics which can unload unnecessary stress.
- Spine & Core Rehabilitation
- Strength & Conditioning Programme
- Pain Management
- Biomechanical Assessment
- Sports Physiotherapy
- Group Class

Sports Injuries
Rolled ankles, jarred knees, impinged shoulders are few conditions in the plethora of sports injuries which can hamper performance and limit our enjoyment of sports. Physiotherapy not only treats the symptoms of these conditions but propels your overall fitness to greater heights.
- Strength & Conditioning Programme
- Pain Management
- Biomechanical Assessment
- Sports Physiotherapy
- Shockwave Therapy
- Group Class

Work Desk Injuries
Conditions such as stiffness, postural abnormalities and muscle overuse from prolonged desk work at the office or home is more prevalent than most would think. We provide the necessary tools to fix you up and educate you on ergonomics which can unload unnecessary stress.

Pre-Post-Surgical Conditions
Surgery involves going through preparation both before and after. Physiotherapists play a vital role in getting your body ready for surgeries with circulatory, breathing and strengthening exercises. After the procedure, let us be there for your recovery and rehabilitation, taking it one step at a time.
Scoliosis & Postural Abnormalities
The way we stand, sit, walk and sleep has influence over our posture and the overall balance of muscles controlling its alignment. A comprehensive screening can be done by our physiotherapists to detect abnormalities, which we will aid in correcting.

Neurological Conditions
Neurological disabilities such as stroke, nerve compression and neuropathies can be barriers for patients to live life to its fullest. We at Synapse are committed to help you overcome these hurdles by ensuring functional mobility and quality of life is at its optimum by providing the right treatment and exercises.

Osteoarthritis & Rheumatism
Joint degeneration and inflammation happens as the human body grows older, but that does not mean our way of life degenerates as well. Relief your joint pains with a joint effort together with your physiotherapist, who will provide pain-relief treatments and prescribe exercises for your wellbeing.

Conditions Relating To Elderly
Common conditions in the older age population include hips & knee pain, back & neck pain, osteoarthritis, rheumatism, fear of falling and many more. Aging and degeneration of bodily function is inevitable, but here at Synapse, we will help you live the best of your life.

Home Physiotherapy
We understand that some conditions or injuries can make it difficult to receive rehabilitation at our clinic be it mobility or transportation issues. Our objective is to provide you with the same high-quality physiotherapy services at home that you would receive in-clinic.
