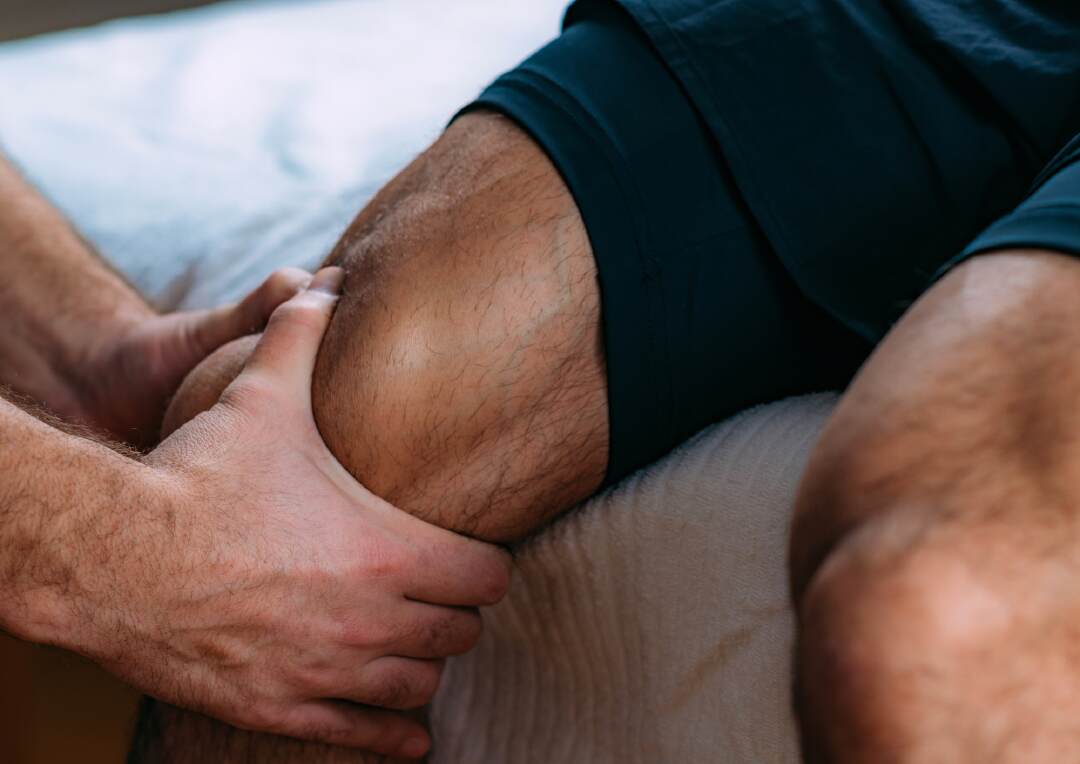
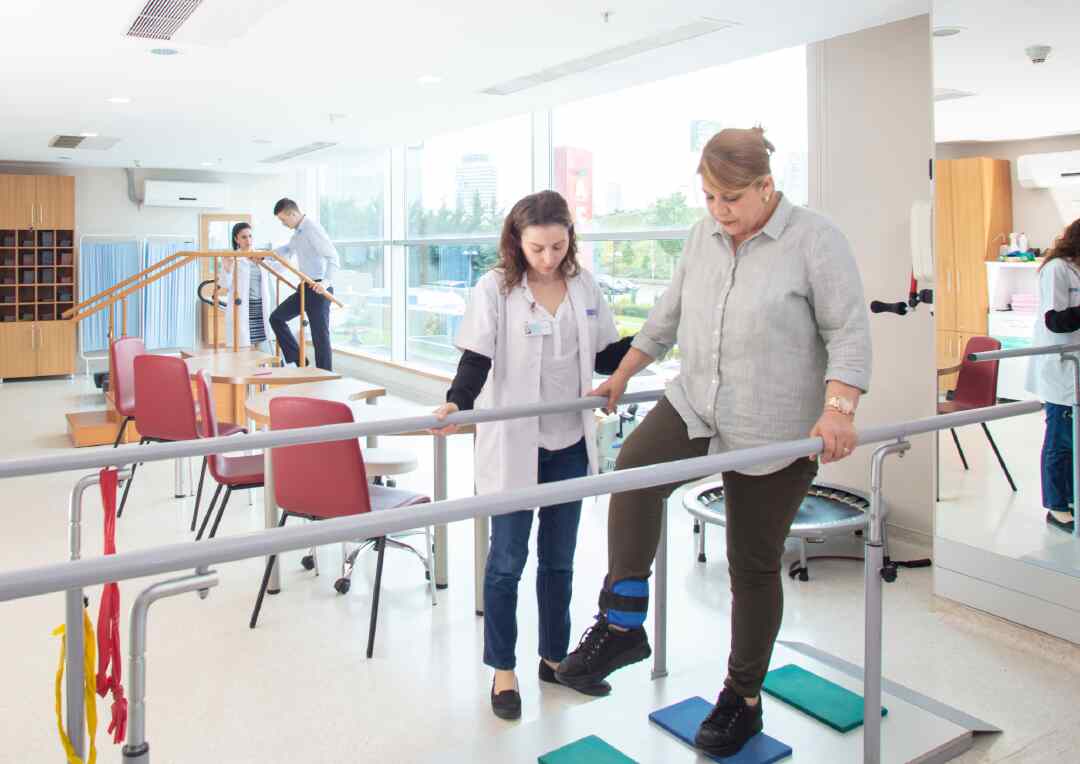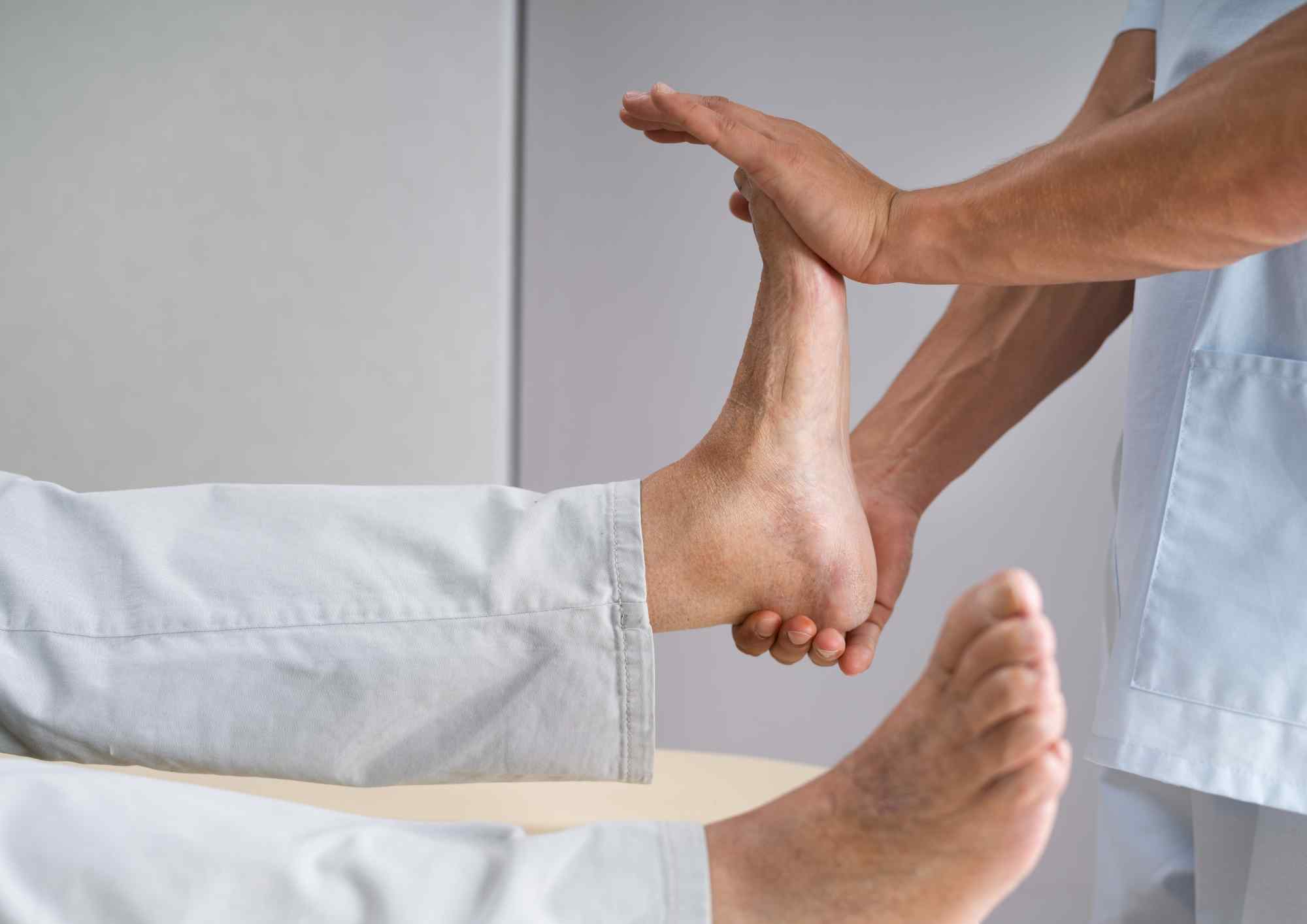

What is a sport massage?
Sports massage is an intense method of soft tissue mobilization that can be advantageous in both athletic and non-athletic settings. It involves several techniques such as effleurage, kneading, wringing, hacking, and trigger point therapy. The goal of sports massage is to relax the musculoskeletal system and target specific areas of concern. This massage technique aids in relieving muscle tension, breaking down adhesions, mobilizing soft tissues, and alleviating pain.
How often and why should you go for a sports massage?
As an athlete or sportsperson, incorporating pre-event and post-event sports massages into your training regimen is crucial for optimal preparation.
Pre-event
A post-event sports massage is typically administered immediately after the event or physical activity and plays a vital role in the recovery process. The purpose of this massage is not only to soothe sore muscles but also to promote a faster return to regular training or competition by aiding the body’s recovery from the stresses of physical exertion. Post-event massage focuses on a more gentle, calming approach to help the body wind down after intense activity. It primarily aims to address the physical strain placed on the musculoskeletal system during the event, prevent muscle cramping, and facilitate overall recovery.
One of the key benefits of post-event massage is its ability to reduce delayed-onset muscle soreness (DOMS), which often occurs after high-intensity exercise. DOMS can lead to stiffness, discomfort, and reduced range of motion in the days following a strenuous workout or competition. By promoting blood flow to the affected muscles, post-event massage helps flush out metabolic waste products such as lactic acid that can accumulate during prolonged or intense exercise. This removal of waste products reduces the likelihood of muscle soreness and cramping, allowing the athlete to recover more comfortably and quickly.
Additionally, post-event massage assists in restoring the body’s normal range of motion by addressing muscle tightness and tension that can develop during physical exertion. During intense exercise, muscles are often pushed to their limits, leading to a loss of flexibility and joint stiffness. By gently mobilizing soft tissues and promoting relaxation, post-event massage helps re-establish flexibility, allowing for a quicker return to regular movement patterns and training. This improved mobility not only speeds up recovery but also reduces the risk of injury in subsequent training sessions by ensuring that the body is in a balanced and functional state.
Furthermore, a well-executed post-event massage helps in rebalancing the body and replenishing the musculoskeletal system after intense exertion. This is especially important for athletes who regularly engage in high-impact or endurance sports, as their muscles and joints often endure significant wear and tear. By focusing on areas of tightness, discomfort, or muscle imbalances, the massage helps to alleviate tension, break down any adhesions or knots, and prevent long-term issues such as chronic stiffness or pain. This process not only aids in immediate recovery but also enhances long-term athletic performance by preventing overuse injuries and maintaining muscular health.
Incorporating regular post-event massages into an athlete’s routine is a proactive approach to maintaining physical well-being. By aiding in the recovery process, post-event massage enables athletes to resume training or competition more quickly, with reduced fatigue and discomfort. It helps rejuvenate the body, preparing it for future events and preventing injury by addressing any underlying issues caused by physical exertion. For athletes of all levels, post-event massage is an essential tool in promoting faster recovery, enhancing physical performance, and ensuring long-term injury prevention.
Post-event
Suppose you’re experiencing pain from an injury like a sprain, strain, or fracture. In that case, a physiotherapist can assist in your recovery after your doctor’s initial treatment by prescribing exercises and therapies that help restore your strength, flexibility, and range of motion. Additionally, if your injury resulted from a fall, a physiotherapist can work with you to enhance your balance and coordination, reducing the risk of future falls and further injury.
For instance, if you’ve recently fractured your ankle in a fall, a physiotherapist can create a personalized exercise program aimed at improving balance, proprioception, and coordination. Exercises such as standing on one leg, walking heel-to-toe, and practicing weight shifts can enhance your balance and decrease the likelihood of future falls. This is especially crucial for older adults, as falls often lead to injury, reduced mobility, and a lower quality of life.
If you suddenly experience severe pain, such as waking up with intense neck pain or suddenly developing severe lower back pain that disrupts your daily activities, work, or sleep, it’s advisable to seek prompt evaluation from a physiotherapist. They can assess your condition, recommend strategies to relieve your pain, and help you regain full function as swiftly as possible. Additionally, they may screen for any signs of serious underlying medical issues that could require further medical evaluation.
If your pain persists despite rest or over-the-counter medications, it’s important to consult a physiotherapist. They can identify the underlying cause of your pain and offer targeted treatment to relieve it.
For instance, Achilles tendon pain might improve with rest but could return when you resume activities like running. In such situations, a physiotherapist can develop a rehabilitation plan to address the issue and help prevent its recurrence.
Key factors to determine the frequency of sports massage session
- Activity level
The frequency of sports massages largely depends on your level of physical activity and training intensity.
Elite Athlete
For professional athletes or those undergoing intense training, sports massages may be beneficial as frequently as 1–3 times per week. Their demanding training schedules often result in muscle tightness, fatigue, and a higher risk of injury. Frequent massages are crucial in keeping the muscles loose, promoting faster recovery, and maintaining optimal performance levels. Regular treatment helps manage the accumulated strain from constant physical exertion, ensuring the body remains in top condition for continued training or competition.
Regular Exercisers
Individuals who engage in moderate physical activity multiple times a week, such as those who work out regularly at the gym or participate in sports, can benefit from bi-weekly or monthly sports massages. This frequency is often sufficient to manage muscle tension, speed up recovery, and prevent injuries. By integrating a sports massage into their routine, regular exercisers can maintain muscle health, address minor aches before they escalate, and enhance overall performance in their workouts.
Weekend Warriors
For those who engage in physical activity on weekends or occasionally, such as recreational athletes or casual sports participants, a monthly sports massage is typically enough. Since their physical demands are not as frequent, this schedule helps alleviate any residual muscle soreness and maintain flexibility. A monthly session can address any tension or strain that builds up over time, ensuring that muscles remain healthy and ready for future activities.
2.Training Intensity
The intensity of your workouts is a key factor in determining how often you should receive sports massages. High-intensity workouts place significant stress on your muscles. This increased strain elevates the need for regular massages to prevent muscle fatigue, reduce soreness, and improve recovery.
- High-Intensity Training
If your routine involves strenuous activities like weightlifting, HIIT, or competitive sports, scheduling weekly or bi-weekly sports massages is recommended. Regular massages help keep your muscles flexible, reduce the risk of overuse injuries, and support optimal performance by addressing the microtears and tightness that result from intense training.
- Moderate Intensity
For those engaging in moderate-intensity activities such as jogging, swimming, or cycling, a monthly sports massage may be sufficient. These sessions help maintain muscle balance, prevent minor tightness from becoming more serious, and promote relaxation. Moderate-intensity athletes benefit from periodic massages to keep muscles functional and ready for continued training.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A typical sports massage lasts between 30 and 60 minutes, depending on the athlete’s needs and the intensity of the session.
No, sports massages complement stretching by addressing deeper muscle layers, while stretching maintains flexibility and joint mobility.
Absolutely. Sports massages benefit anyone experiencing muscle tension, whether from physical activity, prolonged sitting, or everyday stress.
Pre-event massages should be scheduled within 24 hours of the activity to ensure muscles are primed without inducing fatigue.
Persistent muscle soreness, reduced range of motion, or tightness during activities are clear signs you could benefit from a session.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the frequency and timing of sports massages depend on factors such as your activity level, training intensity, and specific recovery goals. It’s important to listen to your body and consult with a qualified physiotherapist to develop a personalized massage plan tailored to your individual needs. For expert guidance and tailored care, you can receive these services at Synapse Physiotherapy.
Produced by MYSense
Tags :

Back & Neck Pain
- Spine & Core Rehabilitation
- Strength & Conditioning Programme
- Pain Management
- Biomechanical Assessment
- Sports Physiotherapy
- Group Class

Sports Injuries
- Strength & Conditioning Programme
- Pain Management
- Biomechanical Assessment
- Sports Physiotherapy
- Shockwave Therapy
- Group Class

Work Desk Injuries

Pre-Post-Surgical Conditions
Scoliosis & Postural Abnormalities

Neurological Conditions

Osteoarthritis & Rheumatism
Joint degeneration and inflammation happens as the human body grows older, but that does not mean our way of life degenerates as well. Relief your joint pains with a joint effort together with your physiotherapist, who will provide pain-relief treatments and prescribe exercises for your wellbeing.

Conditions Relating To Elderly
Common conditions in the older age population include hips & knee pain, back & neck pain, osteoarthritis, rheumatism, fear of falling and many more. Aging and degeneration of bodily function is inevitable, but here at Synapse, we will help you live the best of your life.










